1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
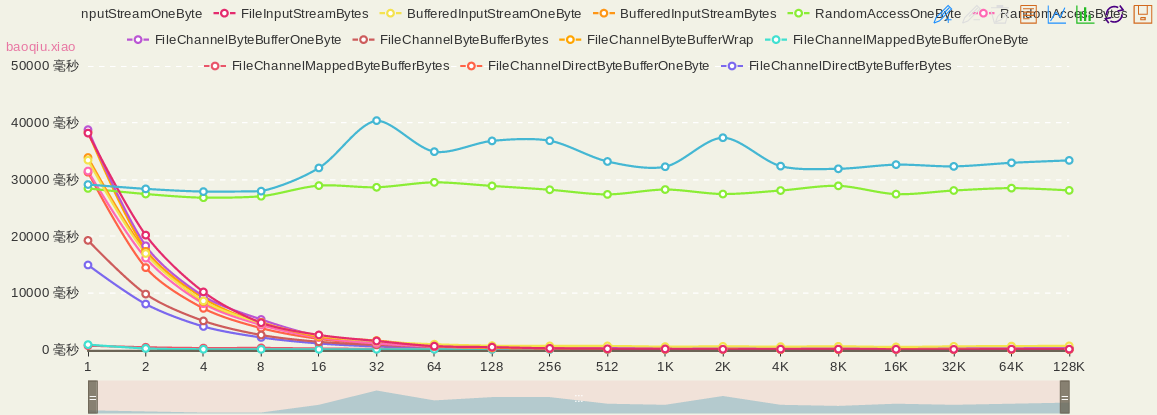
| option = {
title : {
text: 'how_to_read_file_quickly',
subtext: 'baoqiu.xiao'
},
tooltip : {
trigger: 'axis'
},
legend: {
data:['FileInputStreamOneByte','FileInputStreamBytes','BufferedInputStreamOneByte','BufferedInputStreamBytes','RandomAccessOneByte','RandomAccessBytes','FileChannelByteBufferOneByte','FileChannelByteBufferBytes','FileChannelByteBufferWrap','FileChannelMappedByteBufferOneByte','FileChannelMappedByteBufferBytes','FileChannelDirectByteBufferOneByte','FileChannelDirectByteBufferBytes']
},
dataZoom : {
show : true,
realtime: true,
start : 0,
end : 30
},
toolbox: {
show : true,
feature : {
saveAsImage : {show: true}
}
},
calculable : true,
xAxis : [
{
type : 'category',
boundaryGap : false,
data : ['1','2','4','8','16','32','64','128','256','512','1K','2K','4K','8K','16K','32K','64K','128K']
}
],
yAxis : [
{
type : 'value',
axisLabel : {
formatter: '{value} 毫秒'
}
}
],
series : [
{
name:'FileInputStreamOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[29119,28353,27872,27950,32035,40377,34904,36804,36835,33177,32252,37362,32359,31892,32621,32312,32943,33369]
},
{
name:'FileInputStreamBytes',
type:'line',
data:[38182,20208,10194,4768,2616,1551,645,471,262,183,150,100,118,125,96,83,124,110]
},
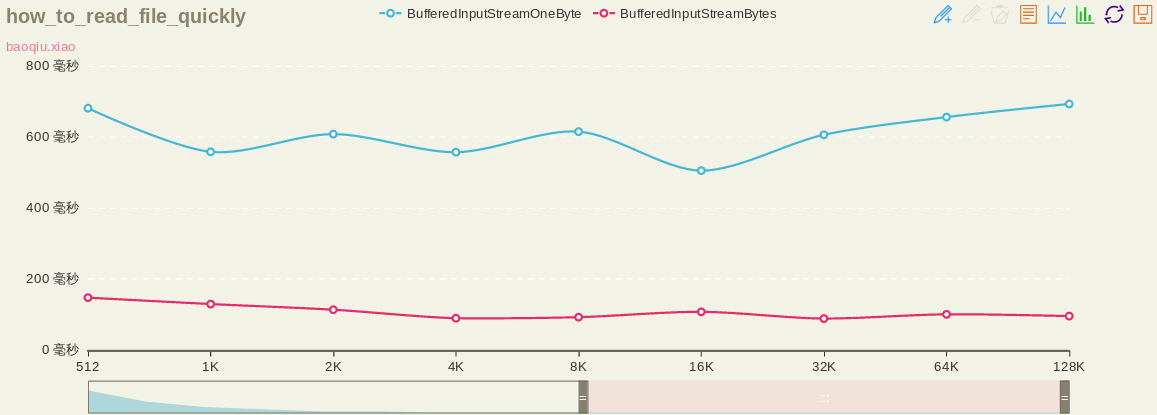
{
name:'BufferedInputStreamOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[33404,16966,8613,4718,2525,1491,980,728,677,681,558,608,557,615,505,606,656,693]
},
{
name:'BufferedInputStreamBytes',
type:'line',
data:[33880,17333,8487,4851,2293,1632,627,358,242,147,129,113,89,92,107,88,100,95]
},
{
name:'RandomAccessOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[28430,27445,26794,27053,28929,28633,29509,28870,28195,27376,28236,27444,28061,28889,27423,28064,28481,28084]
},
{
name:'RandomAccessBytes',
type:'line',
data:[31497,16162,8135,4365,2131,1117,561,321,193,146,110,101,109,87,89,91,102,96]
},
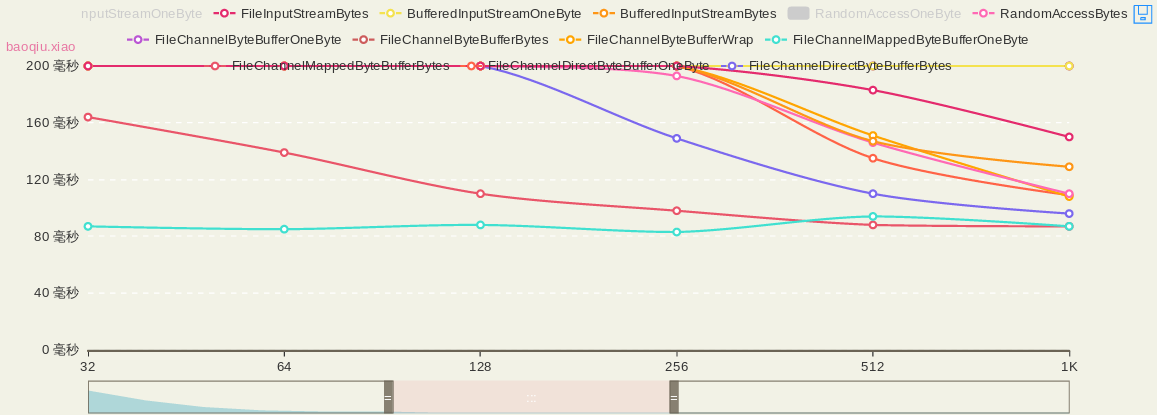
{
name:'FileChannelByteBufferOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[38778,18325,9447,5344,2430,1413,779,507,380,310,298,259,267,263,249,264,260,258]
},
{
name:'FileChannelByteBufferBytes',
type:'line',
data:[19279,9823,5090,2605,1407,854,577,380,333,272,272,239,237,241,237,234,249,270]
},
{
name:'FileChannelByteBufferWrap',
type:'line',
data:[38382,17636,9094,4608,2327,1198,646,355,249,151,108,100,92,90,88,103,85,92]
},
{
name:'FileChannelMappedByteBufferOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[913,240,92,83,82,87,85,88,83,94,87,90,81,124,81,84,83,120]
},
{
name:'FileChannelMappedByteBufferBytes',
type:'line',
data:[731,447,305,332,225,164,139,110,98,88,87,140,97,86,93,92,92,92]
},
{
name:'FileChannelDirectByteBufferOneByte',
type:'line',
data:[31287,14473,7296,3815,1919,1001,547,319,200,135,109,98,84,77,80,82,77,86]
},
{
name:'FileChannelDirectByteBufferBytes',
type:'line',
data:[14945,8060,4107,2174,1120,580,334,206,149,110,96,95,79,89,81,81,86,84]
}
]
};
|